Hello every one,
I start in the world of programming with TTN.
I am developing a hive project connected with an esp32 and RFM95 module through my Raspberry Gateway sending data to node red and blynk application. I block for several days on sending data. I use a BME280 sensor with which I send temperature and humidity. Everything works correctly and I receive it to blynk but when I want to add a data like altitude I do not receive anything. I can’t understand why and especially how sflt16 datum is working. I read a lot of thinks but it’s too complicated for me to understand…
I try to understand this : https://www.thethingsnetwork.org/docs/devices/bytes.html#how-to-send-big-numbers
but the code I have is different…
My code is:
#include <lmic.h>
#include <hal/hal.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include <Adafruit_BME280.h>
//BME sensor
#define SEALEVELPRESSURE_HPA (1013.25)
Adafruit_BME280 bme; // I2C
//
// For normal use, we require that you edit the sketch to replace FILLMEIN
// with values assigned by the TTN console. However, for regression tests,
// we want to be able to compile these scripts. The regression tests define
// COMPILE_REGRESSION_TEST, and in that case we define FILLMEIN to a non-
// working but innocuous value.
//
#ifdef COMPILE_REGRESSION_TEST
# define FILLMEIN 0
#else
# warning "You must replace the values marked FILLMEIN with real values from the TTN control panel!"
# define FILLMEIN (#dont edit this, edit the lines that use FILLMEIN)
#endif
// LoRaWAN NwkSKey, network session key
static const PROGMEM u1_t NWKSKEY[16] = { ##, ## };
// LoRaWAN AppSKey, application session key
static const u1_t PROGMEM APPSKEY[16] = { ##, ## };
// LoRaWAN end-device address (DevAddr)
// See http://thethingsnetwork.org/wiki/AddressSpace
// The library converts the address to network byte order as needed.
#ifndef COMPILE_REGRESSION_TEST
static const u4_t DEVADDR = #######;
#else
static const u4_t DEVADDR = 0;
#endif
// These callbacks are only used in over-the-air activation, so they are
// left empty here (we cannot leave them out completely unless
// DISABLE_JOIN is set in arduino-lmic/project_config/lmic_project_config.h,
// otherwise the linker will complain).
void os_getArtEui (u1_t* buf) { }
void os_getDevEui (u1_t* buf) { }
void os_getDevKey (u1_t* buf) { }
// payload to send to TTN gateway
static uint8_t payload[5];
static osjob_t sendjob;
// Schedule TX every this many seconds (might become longer due to duty
// cycle limitations).
const unsigned TX_INTERVAL = 30;
// Pin mapping for Adafruit Feather M0 LoRa
const lmic_pinmap lmic_pins = {
.nss = 5,
.rxtx = LMIC_UNUSED_PIN,
.rst = 13,
// LBT cal for the Adafruit Feather M0 LoRa, in dB
.dio = {12, 14, LMIC_UNUSED_PIN}
};
void onEvent (ev_t ev) {
Serial.print(os_getTime());
Serial.print(": ");
switch(ev) {
case EV_SCAN_TIMEOUT:
Serial.println(F("EV_SCAN_TIMEOUT"));
break;
case EV_BEACON_FOUND:
Serial.println(F("EV_BEACON_FOUND"));
break;
case EV_BEACON_MISSED:
Serial.println(F("EV_BEACON_MISSED"));
break;
case EV_BEACON_TRACKED:
Serial.println(F("EV_BEACON_TRACKED"));
break;
case EV_JOINING:
Serial.println(F("EV_JOINING"));
break;
case EV_JOINED:
Serial.println(F("EV_JOINED"));
break;
/*
|| This event is defined but not used in the code. No
|| point in wasting codespace on it.
||
|| case EV_RFU1:
|| Serial.println(F("EV_RFU1"));
|| break;
*/
case EV_JOIN_FAILED:
Serial.println(F("EV_JOIN_FAILED"));
break;
case EV_REJOIN_FAILED:
Serial.println(F("EV_REJOIN_FAILED"));
break;
case EV_TXCOMPLETE:
Serial.println(F("EV_TXCOMPLETE (includes waiting for RX windows)"));
if (LMIC.txrxFlags & TXRX_ACK)
Serial.println(F("Received ack"));
if (LMIC.dataLen) {
Serial.println(F("Received "));
Serial.println(LMIC.dataLen);
Serial.println(F(" bytes of payload"));
}
// Schedule next transmission
os_setTimedCallback(&sendjob, os_getTime()+sec2osticks(TX_INTERVAL), do_send);
break;
case EV_LOST_TSYNC:
Serial.println(F("EV_LOST_TSYNC"));
break;
case EV_RESET:
Serial.println(F("EV_RESET"));
break;
case EV_RXCOMPLETE:
// data received in ping slot
Serial.println(F("EV_RXCOMPLETE"));
break;
case EV_LINK_DEAD:
Serial.println(F("EV_LINK_DEAD"));
break;
case EV_LINK_ALIVE:
Serial.println(F("EV_LINK_ALIVE"));
break;
/*
|| This event is defined but not used in the code. No
|| point in wasting codespace on it.
||
|| case EV_SCAN_FOUND:
|| Serial.println(F("EV_SCAN_FOUND"));
|| break;
*/
case EV_TXSTART:
Serial.println(F("EV_TXSTART"));
break;
default:
Serial.print(F("Unknown event: "));
Serial.println((unsigned) ev);
break;
}
}
void do_send(osjob_t* j){
// Check if there is not a current TX/RX job running
if (LMIC.opmode & OP_TXRXPEND) {
Serial.println(F("OP_TXRXPEND, not sending"));
} else {
// read the temperature from the DHT22
float Temperature = bme.readTemperature();
Serial.print("Temperature: "); Serial.print(Temperature);
Serial.println(" *C");
// adjust for the f2sflt16 range (-1 to 1)
Temperature = Temperature / 100;
// read the humidity from the DHT22
float Humidity = bme.readHumidity();
Serial.print("humidité: ");Serial.print(Humidity);
Serial.println("% ");
// adjust for the f2sflt16 range (-1 to 1)
Humidity = Humidity / 100;
// float Altitude = bme.readAltitude(SEALEVELPRESSURE_HPA);
float Altitude = 100;
Serial.print("Approx. Altitude = ");
Serial.print(Altitude);
Serial.println(" m");
Altitude = Altitude / 100;
// float -> int
// note: this uses the sflt16 datum (https://github.com/mcci-catena/arduino-lmic#sflt16)
uint16_t payloadTemp = LMIC_f2sflt16(Temperature);
// int -> bytes
byte tempLow = lowByte(payloadTemp);
byte tempHigh = highByte(payloadTemp);
Serial.print("payloadTemp= ");
Serial.println(payloadTemp);
Serial.print("tempLow= ");
Serial.println(tempLow);
Serial.print("tempHigh= ");
Serial.println(tempHigh);
// place the bytes into the payload
payload[0] = tempLow;
payload[1] = tempHigh;
// float -> int
uint16_t payloadHumid = LMIC_f2sflt16(Humidity);
// int -> bytes
byte humidLow = lowByte(payloadHumid);
byte humidHigh = highByte(payloadHumid);
payload[2] = humidLow;
payload[3] = humidHigh;
// float -> int
uint16_t payloadAlt = LMIC_f2sflt16(Altitude);
// int -> bytes
byte altLow = lowByte(payloadAlt);
byte altHigh = highByte(payloadAlt);
payload[4] = altLow;
payload[5] = altHigh;
// prepare upstream data transmission at the next possible time.
// transmit on port 1 (the first parameter); you can use any value from 1 to 223 (others are reserved).
// don't request an ack (the last parameter, if not zero, requests an ack from the network).
// Remember, acks consume a lot of network resources; don't ask for an ack unless you really need it.
LMIC_setTxData2(1, payload, sizeof(payload)-1, 0);
}
// Next TX is scheduled after TX_COMPLETE event.
}
void setup() {
delay(4000);
while (!Serial);
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(100);
Serial.println(F("Starting"));
bme.begin(0x76);
// LMIC init
os_init();
// Reset the MAC state. Session and pending data transfers will be discarded.
LMIC_reset();
// Set static session parameters. Instead of dynamically establishing a session
// by joining the network, precomputed session parameters are be provided.
// On AVR, these values are stored in flash and only copied to RAM
// once. Copy them to a temporary buffer here, LMIC_setSession will
// copy them into a buffer of its own again.
uint8_t appskey[sizeof(APPSKEY)];
uint8_t nwkskey[sizeof(NWKSKEY)];
memcpy_P(appskey, APPSKEY, sizeof(APPSKEY));
memcpy_P(nwkskey, NWKSKEY, sizeof(NWKSKEY));
LMIC_setSession (0x13, DEVADDR, nwkskey, appskey);
#if defined(CFG_eu868) // EU channel setup
int channel = 0;
int dr = DR_SF7;
for(int i=0; i<9; i++) {
if(i != channel) {
LMIC_disableChannel(i);
}
}
// Set data rate (SF) and transmit power for uplink
LMIC_setDrTxpow(dr, 14); // g-band
#elif defined(CFG_us915) // US channel setup
// Instead of using selectSubBand, which will cycle through a sub-band of 8
// channels. We'll configure the device to only use one frequency.
// First disable all sub-bands
for (int b = 0; b < 8; ++b) {
LMIC_disableSubBand(b);
}
// Then enable the channel(s) you want to use
//LMIC_enableChannel(8); // 903.9 MHz
LMIC_enableChannel(17);
#endif
// Disable link check validation
LMIC_setLinkCheckMode(0);
// TTN uses SF9 for its RX2 window.
LMIC.dn2Dr = DR_SF9;
// Set data rate and transmit power for uplink
LMIC_setDrTxpow(DR_SF7,14);
// Start job
do_send(&sendjob);
}
void loop() {
os_runloop_once();
}
My payload format is:
function Decoder(bytes, port) {
// Decode an uplink message from a buffer
// (array) of bytes to an object of fields.
var decoded = {};
// temperature
rawTemp = bytes[0] + bytes[1] * 256;
decoded.degreesC = sflt162f(rawTemp) * 100;
// humidity
rawHumid = bytes[2] + bytes[3] * 256;
decoded.humidity = sflt162f(rawHumid) * 100;
//Altitude
rawAlt = bytes[4] + bytes[5] * 256;
decoded.altitude = sflt162f(rawAlt) * 100;
return decoded;
}
function sflt162f(rawSflt16)
{
// rawSflt16 is the 2-byte number decoded from wherever;
// it's in range 0..0xFFFF
// bit 15 is the sign bit
// bits 14..11 are the exponent
// bits 10..0 are the the mantissa. Unlike IEEE format,
// the msb is transmitted; this means that numbers
// might not be normalized, but makes coding for
// underflow easier.
// As with IEEE format, negative zero is possible, so
// we special-case that in hopes that JavaScript will
// also cooperate.
//
// The result is a number in the open interval (-1.0, 1.0);
//
// throw away high bits for repeatability.
rawSflt16 &= 0xFFFF;
// special case minus zero:
if (rawSflt16 == 0x8000)
return -0.0;
// extract the sign.
var sSign = ((rawSflt16 & 0x8000) !== 0) ? -1 : 1;
// extract the exponent
var exp1 = (rawSflt16 >> 11) & 0xF;
// extract the "mantissa" (the fractional part)
var mant1 = (rawSflt16 & 0x7FF) / 2048.0;
// convert back to a floating point number. We hope
// that Math.pow(2, k) is handled efficiently by
// the JS interpreter! If this is time critical code,
// you can replace by a suitable shift and divide.
var f_unscaled = sSign * mant1 * Math.pow(2, exp1 - 15);
return f_unscaled;
}
I get good temperature and humidity but not altitude and I want to add more sensor like weight sensor.
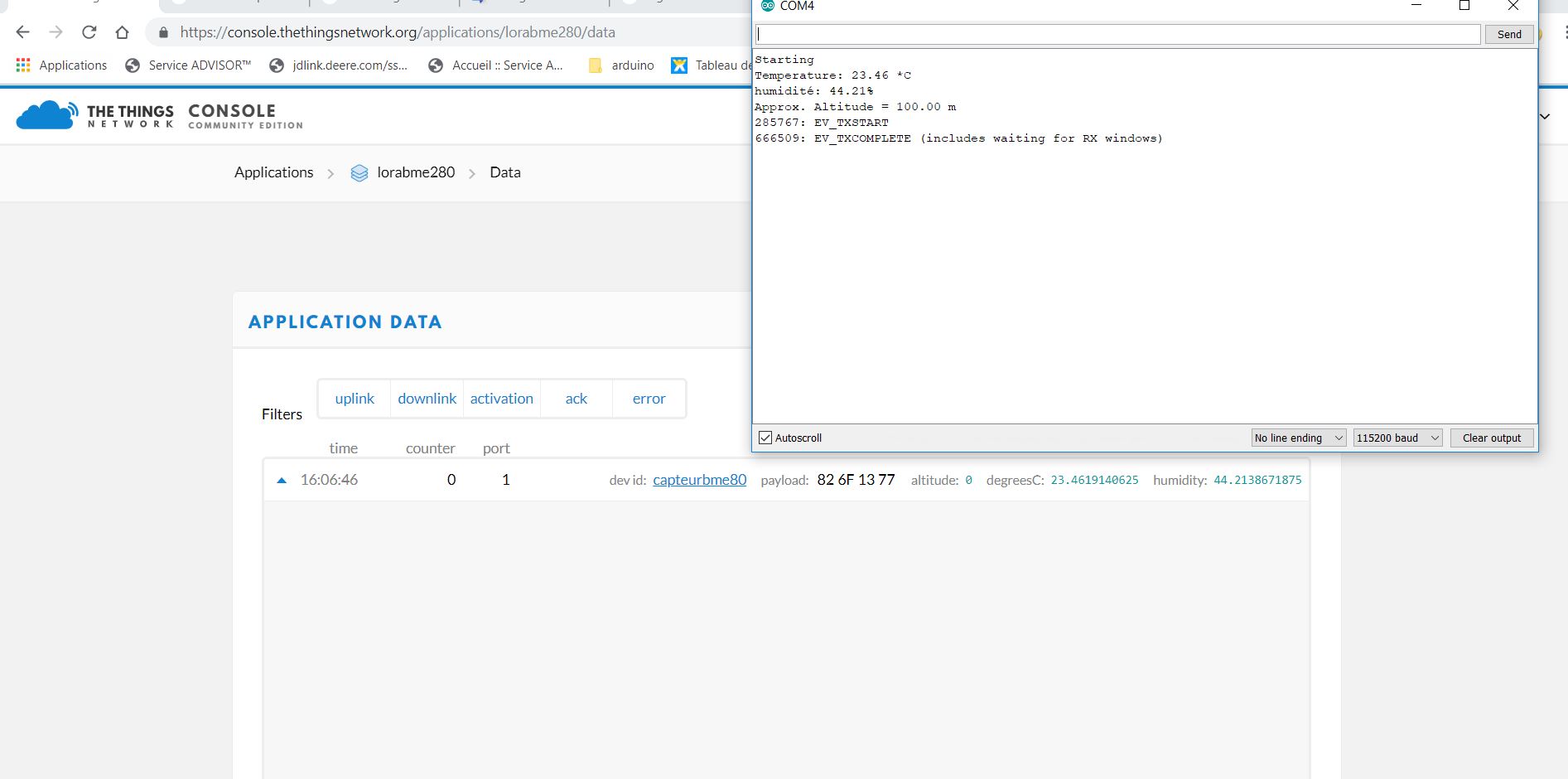
Many thanks for your help
christophe
