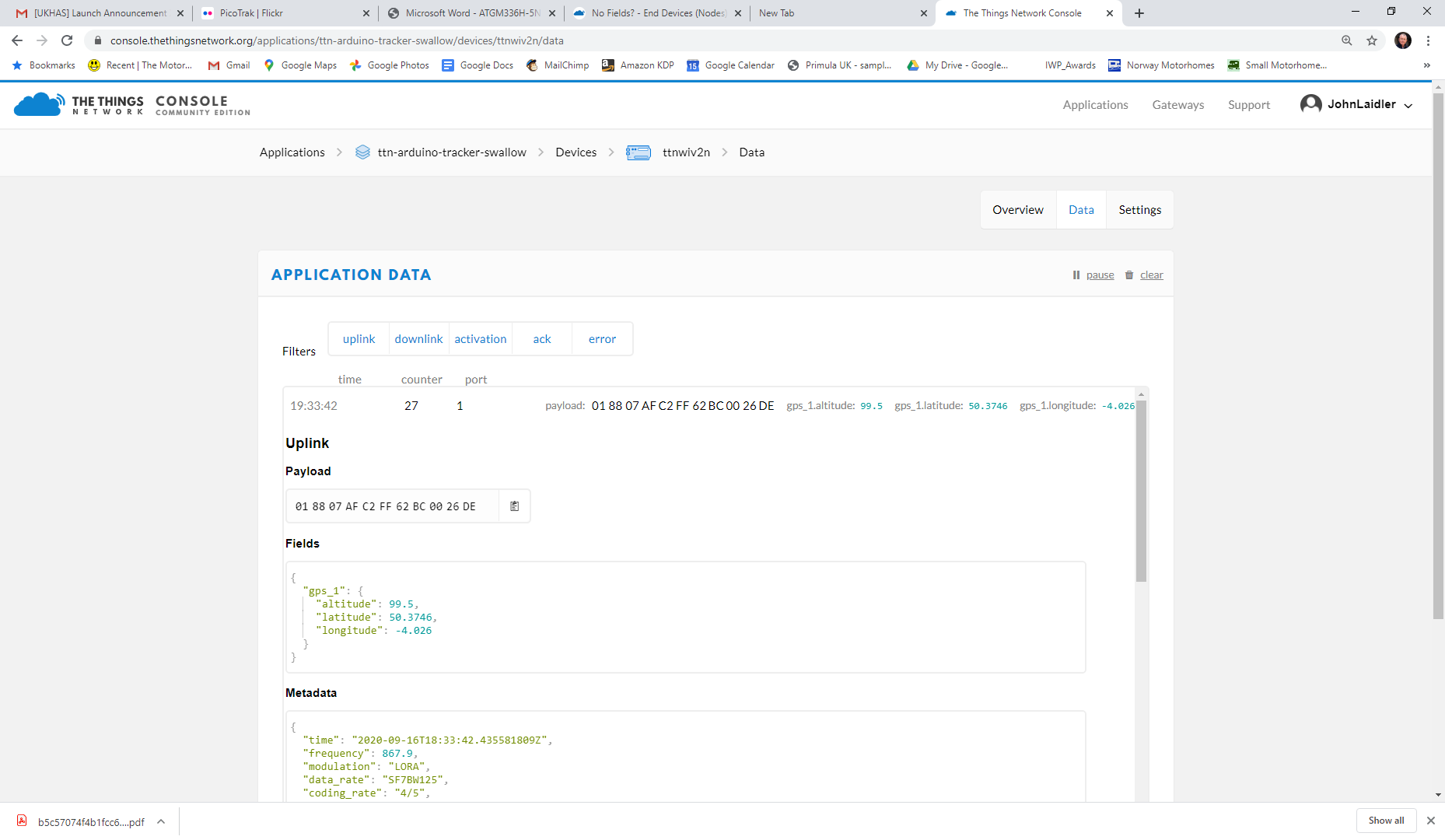
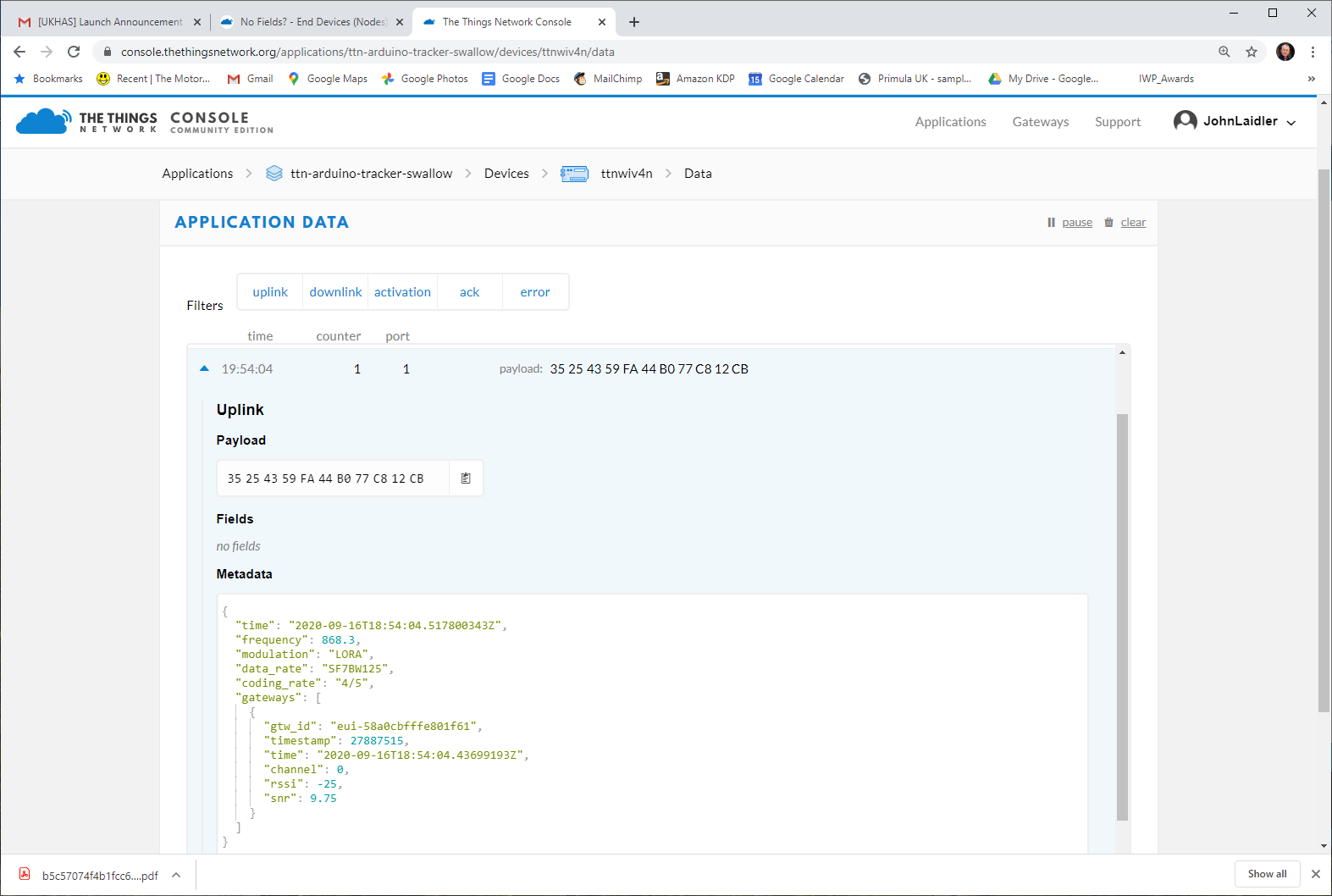
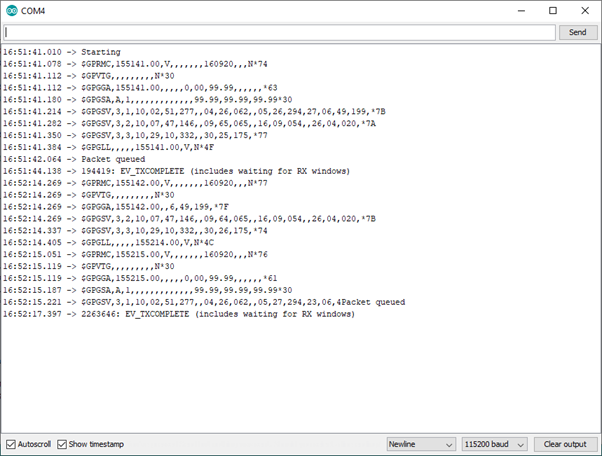
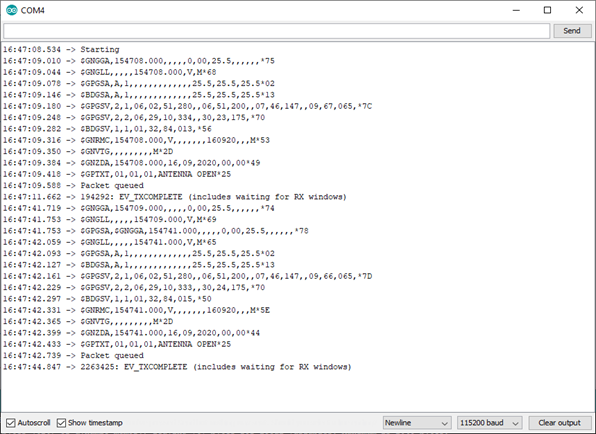
But the data is there in the device because I can print them in the serial console and the values are correct. The curious thing is this software works but not with this new tracker with a different GPS.
The full code is:
#include <lmic.h>
#include <hal/hal.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
#include <AltSoftSerial.h>
#define LPP_GPS 136 // 3 byte lon/lat 0.0001 °, 3 bytes alt 0.01 meter
static const int RXPin = 8, TXPin = 9;
static const uint32_t GPSBaud = 9600;
TinyGPSPlus gps;
AltSoftSerial ss(RXPin, TXPin); // RX, TX
static const PROGMEM u1_t NWKSKEY[16] = { 0xA5, 0x91, 0xE2, 0x6E, 0x63, 0x8F, 0xDA, 0xEC, 0x7E, 0xAD, 0xC4, 0x03, 0x1E, 0x4D, 0xE6, 0x43 };
static const u1_t PROGMEM APPSKEY[16] = { 0x3B, 0x82, 0xA9, 0xAD, 0x67, 0xF0, 0x9B, 0xF7, 0x11, 0x44, 0x44, 0xC8, 0x8C, 0x62, 0xEC, 0xFA };
static const u4_t DEVADDR = 0x(removed); // <-- Change this address for every node!
const unsigned TX_INTERVAL = 30;
void os_getArtEui (u1_t* buf) { }
void os_getDevEui (u1_t* buf) { }
void os_getDevKey (u1_t* buf) { }
uint8_t coords[11];
static osjob_t sendjob;
static osjob_t initjob;
uint8_t cursor = 0;
uint8_t channel;
// Pin mapping
const lmic_pinmap lmic_pins = {
.nss = 10,
.rxtx = LMIC_UNUSED_PIN,
.rst = LMIC_UNUSED_PIN,
.dio = {4, 5, 7},
};
//TinyGPSInteger satellites; //not sure if this necessary
void get_coords () {
bool newData = false;
unsigned long chars;
unsigned short sentences, failed;
//float flat,flon,faltitudeGPS,fhdopGPS; //add satellites
float flat,flon,faltitudeGPS;
//satellites is an integer
unsigned short int fsatellitesGPS;
unsigned long age;
// For one second we parse GPS data and report some key values
for (unsigned long start = millis(); millis() - start < 1000;) {
while (ss.available()) {
char c = ss.read();
Serial.write(c); // uncomment this line if you want to see the GPS data flowing
if (gps.encode(c)) { // Did a new valid sentence come in?
newData = true;
}
}
}
if ( newData ) {
flat=gps.location.lat();
flon=gps.location.lng();
Serial.println("latitude");
Serial.println(gps.location.lat());
Serial.println("longitude");
Serial.println(gps.location.lng());
Serial.println("altitude");
Serial.println(gps.altitude.meters());
if (gps.altitude.isValid())
faltitudeGPS = gps.altitude.meters();
else
faltitudeGPS=0;
if (gps.satellites.isValid())
fsatellitesGPS = gps.satellites.value();
else
fsatellitesGPS=0;
Serial.println("satellites");
Serial.println(gps.satellites.value()); //Shows number of satellites - working!
}
int32_t lat = flat * 10000;
int32_t lon = flon * 10000;
int32_t altitudeGPS = faltitudeGPS * 100;
channel = 0x01;
coords[0] = channel;
coords[1] = LPP_GPS;
coords[2] = lat >> 16;
coords[3] = lat >> 8;
coords[4] = lat;
coords[5] = lon >> 16;
coords[6] = lon >> 8;
coords[7] = lon;
coords[8] = altitudeGPS >> 16;
coords[9] = altitudeGPS >> 8;
coords[10] = altitudeGPS;
}
void do_send(osjob_t* j) {
// Check if there is not a current TX/RX job running
if (LMIC.opmode & OP_TXRXPEND) {
Serial.println(F("OP_TXRXPEND, not sending"));
} else {
// Prepare upstream data transmission at the next possible time.
get_coords();
LMIC_setTxData2(1, (uint8_t*) coords, sizeof(coords), 0);
Serial.println(F("Packet queued"));
}
}
// Next TX is scheduled after TX_COMPLETE event.
void onEvent (ev_t ev) {
Serial.print(os_getTime());
Serial.print(": ");
switch(ev) {
case EV_SCAN_TIMEOUT:
Serial.println(F("EV_SCAN_TIMEOUT"));
break;
case EV_BEACON_FOUND:
Serial.println(F("EV_BEACON_FOUND"));
break;
case EV_BEACON_MISSED:
Serial.println(F("EV_BEACON_MISSED"));
break;
case EV_BEACON_TRACKED:
Serial.println(F("EV_BEACON_TRACKED"));
break;
case EV_JOINING:
Serial.println(F("EV_JOINING"));
break;
case EV_JOINED:
Serial.println(F("EV_JOINED"));
// Disable link check validation (automatically enabled
// during join, but not supported by TTN at this time).
LMIC_setLinkCheckMode(0);
break;
case EV_RFU1:
Serial.println(F("EV_RFU1"));
break;
case EV_JOIN_FAILED:
Serial.println(F("EV_JOIN_FAILED"));
break;
case EV_REJOIN_FAILED:
Serial.println(F("EV_REJOIN_FAILED"));
break;
break;
case EV_TXCOMPLETE:
Serial.println(F("EV_TXCOMPLETE (includes waiting for RX windows)"));
if (LMIC.txrxFlags & TXRX_ACK)
Serial.println(F("Received ack"));
if (LMIC.dataLen) {
Serial.println(F("Received "));
Serial.println(LMIC.dataLen);
Serial.println(F(" bytes of payload"));
}
// Schedule next transmission
os_setTimedCallback(&sendjob, os_getTime()+sec2osticks(TX_INTERVAL), do_send);
break;
case EV_LOST_TSYNC:
Serial.println(F("EV_LOST_TSYNC"));
break;
case EV_RESET:
Serial.println(F("EV_RESET"));
break;
case EV_RXCOMPLETE:
// data received in ping slot
Serial.println(F("EV_RXCOMPLETE"));
break;
case EV_LINK_DEAD:
Serial.println(F("EV_LINK_DEAD"));
break;
case EV_LINK_ALIVE:
Serial.println(F("EV_LINK_ALIVE"));
break;
default:
Serial.println(F("Unknown event"));
break;
}
}
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(F("Starting"));
ss.begin(GPSBaud);
// LMIC init
os_init();
// Reset the MAC state. Session and pending data transfers will be discarded.
LMIC_reset();
// Set static session parameters. Instead of dynamically establishing a session
// by joining the network, precomputed session parameters are be provided.
#ifdef PROGMEM
// On AVR, these values are stored in flash and only copied to RAM
// once. Copy them to a temporary buffer here, LMIC_setSession will
// copy them into a buffer of its own again.
uint8_t appskey[sizeof(APPSKEY)];
uint8_t nwkskey[sizeof(NWKSKEY)];
memcpy_P(appskey, APPSKEY, sizeof(APPSKEY));
memcpy_P(nwkskey, NWKSKEY, sizeof(NWKSKEY));
LMIC_setSession (0x1, DEVADDR, nwkskey, appskey);
#else
// If not running an AVR with PROGMEM, just use the arrays directly
LMIC_setSession (0x1, DEVADDR, NWKSKEY, APPSKEY);
#endif
#if defined(CFG_eu868)
// Set up the channels used by the Things Network, which corresponds
// to the defaults of most gateways. Without this, only three base
// channels from the LoRaWAN specification are used, which certainly
// works, so it is good for debugging, but can overload those
// frequencies, so be sure to configure the full frequency range of
// your network here (unless your network autoconfigures them).
// Setting up channels should happen after LMIC_setSession, as that
// configures the minimal channel set.
// NA-US channels 0-71 are configured automatically
LMIC_setupChannel(0, 868100000, DR_RANGE_MAP(DR_SF12, DR_SF7), BAND_CENTI); // g-band
LMIC_setupChannel(1, 868300000, DR_RANGE_MAP(DR_SF12, DR_SF7B), BAND_CENTI); // g-band
LMIC_setupChannel(2, 868500000, DR_RANGE_MAP(DR_SF12, DR_SF7), BAND_CENTI); // g-band
LMIC_setupChannel(3, 867100000, DR_RANGE_MAP(DR_SF12, DR_SF7), BAND_CENTI); // g-band
LMIC_setupChannel(4, 867300000, DR_RANGE_MAP(DR_SF12, DR_SF7), BAND_CENTI); // g-band
LMIC_setupChannel(5, 867500000, DR_RANGE_MAP(DR_SF12, DR_SF7), BAND_CENTI); // g-band
LMIC_setupChannel(6, 867700000, DR_RANGE_MAP(DR_SF12, DR_SF7), BAND_CENTI); // g-band
LMIC_setupChannel(7, 867900000, DR_RANGE_MAP(DR_SF12, DR_SF7), BAND_CENTI); // g-band
LMIC_setupChannel(8, 868800000, DR_RANGE_MAP(DR_FSK, DR_FSK), BAND_MILLI); // g2-band
// TTN defines an additional channel at 869.525Mhz using SF9 for class B
// devices' ping slots. LMIC does not have an easy way to define set this
// frequency and support for class B is spotty and untested, so this
// frequency is not configured here.
#elif defined(CFG_us915)
// NA-US channels 0-71 are configured automatically
// but only one group of 8 should (a subband) should be active
// TTN recommends the second sub band, 1 in a zero based count.
// https://github.com/TheThingsNetwork/gateway-conf/blob/master/US-global_conf.json
LMIC_selectSubBand(1);
#endif
// Disable link check validation
LMIC_setLinkCheckMode(0);
// TTN uses SF9 for its RX2 window.
LMIC.dn2Dr = DR_SF9;
// Set data rate and transmit power for uplink (note: txpow seems to be ignored by the library)
LMIC_setDrTxpow(DR_SF7,14);
// Start job
do_send(&sendjob);
}
void loop() {
os_runloop_once();
}